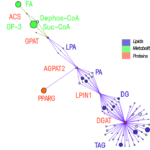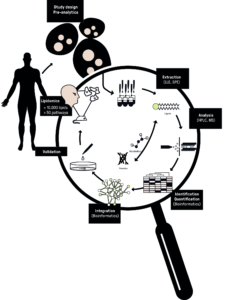
The lipidomics workflow
Lipidomics
Even with a lipid content of over 10% in the human body, lipids were not in the central scientific focus during the last decade. However, more and more evidence is provided that non-genetically determined biomolecules such as metabolites and lipids are the key to biomolecular regulation. Today it is obvious that lipids are not only important for energy homeostasis and as an environmental-cellular barrier, but also represent a central part of our signal transduction machinery. Disruptions of the sensitive lipid metabolism are highly correlated with different types of diseases including thrombocytopenia, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, obesity and hyperlipidemia. This is especially true for the latter ones, which are also reaching pandemic levels, causing a larger annual health burden than infectious diseases. Therefore, lipid metabolism is again becoming an emerging scientific field and is a central part of pharmacological research today (statins, cyclooxygenase inhibitors). Therefore the mission of the Lipidomics group in Vienna is to understand lipids in context with their proteins (enzymes) and building blocks (metabolites) in a true systems biology way.News
Markus Hartl Advancing proteomics step-by-step
On January 23, 2025, the institute seminar will take place:January 23, 2025 / 12:00 / HS2Markus Hartl Max Perutz Labs Vienna“Advancing …
Boryana Petrova “Leveraging Metabolomics to Charakterize Embryonic CSF During Inflammation”
On January 16, 2025, the institute seminar will take place:January 16, 2025 / 12:00 / HS2Boryana PetrovaMedical University of Vienna”Leveraging …
Projects
Adipogenesis
The rising prevalence of obesity globally presents a critical social challenge, threatening to reverse the progress made in life …

Computational Lipidomics
Platelet Lipidomics
Lipid signaling & metabolism in platelets Platelet integrity and function critically depend on lipid composition. However, the lipid inventory in …

Neurolipidomics